Virtual Private Network (VPN)
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (498.65 KB, 41 trang )
Virtual Private Network
(VPN)
NỘI DUNG
Nguyên lý VPN
Các biến đổi đóng gói trong VPNs
Mã hoá trong VPNs
Xác thực trong VPNs
Ưu nhược điểm của VPNs
2
VPN CONCEPTS
Virtual Private Network (VPN) giải quyết các
vấn đề:
Tạo liên kết an toàn trên kênh truyền dữ liệu không
an toàn
Mã hoá dữ liệu trên kênh truyền
3
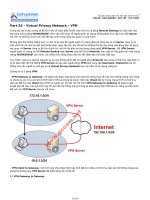
WHAT VPNS ARE
VPN
Kết nối logic ảo
Tạo kết nối an toàn trên kênh Internet
Secure tunnel
Tạo liên kết tổ chức logic giữa các side
Đầu cuối của VPNs
Specified computers, users, or network gateways
4
5
WHY ESTABLISH A VPN?
Nguyên nhân triển khai
VPNs mạng kết nối an toàn giá rẻ
VPNs provide secure connection for remote users
Contractors
Traveling employees
Partners and suppliers
Thành phần của VPNs (Components)
VPN server or host
Configured to accept connections from clients
VPN client or guest
Endpoints connecting to a VPN
6
WHY ESTABLISH A VPN?
VPN Components
Tunnel
Kết nối mà dữ liệu được truyền qua nó
VPN protocols
Tập hợp các giao thức chuẩn
Mã hoá
Types of VPNs
Sitetosite VPN
Gatewaytogateway VPN
Clienttosite VPN
Remote access VPN
7
WHY ESTABLISH A VPN?
Hardware versus software VPNs
Hardwarebased VPNs
Connect one gateway to another
Routers at each network gateway encrypt and decrypt
packets
VPN appliance
Designed to serve as VPN endpoint
Join multiple LANs
Benefits
Scalable
Better security
8
9
10
WHY ESTABLISH A VPN?
Hardware versus software VPNs
Softwarebased VPNs
Integrated with firewalls
Appropriate when participating networks use different
routers and firewalls
Benefits
More costeffective
Offer maximum flexibility
11
12
WHY ESTABLISH A VPN?
VPN combinations
Combining VPN hardware with software adds
layers of network security
One useful combination is a VPN bundled with a
firewall
VPNs do not eliminate the need for firewalls
Provide flexibility and versatility
13
WHY ESTABLISH A VPN?
VPN combinations (continued)
Points to consider when selecting VPNs
Compatibility
Scalability
Security
Cost
Vendor support
14
BIếN ĐổI ĐÓNG GÓI TRONG VPN
(ENCAPSULATION)
Các buớc trong tiến trình VPN
Đóng gói (Encapsulation)
Mã hoá (Encryption)
Xác thực (Authentication)
Encapsulation
Đóng gói dữ liệu và các thông số khác nhau
Ví dụ như IP header
Bảo vệ tính nguyên vẹn dữ liệu
15
16