CFA 2018 smart summary, study session 03, reading 12 1
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (94.68 KB, 3 trang )
2017, Study Session # 3, Reading # 12
∝ = Level of Significance
TS = Test Statistics
TV = Table Value
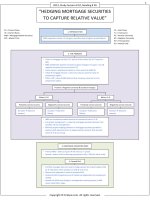
Hypothesis Testing
Procedure
Hypothesis
Statement about
one or more
populations
Null
Hypothesis H0
Tested for
possible
rejection.
Always
includes ‘=’
sign.
SS = Sample Statistic
CV = Critical Value
SE = Standard Error
“HYPOTHESIS TESTING”
Two
Types
Alternative
Hypothesis
Ha
Hypothesis is
accepted
when the null
hypothesis is
rejected.
It is based on sample
statistics & probability
theory.
It is used to determine
whether a hypothesis is a
reasonable statement or
not.
Steps in Hypothesis
Testing
One Tailed Test
Alternative hypothesis
having one side.
Upper Tail
H0:µ ≤ µ0 vs Ha: µ > µ0.
Decision rule
Reject H0 if TS > TV
Lower Tail
H0:µ ≥ µ0 vs Ha: µ < µ0.
Decision rule
Reject H0 if TS < TV
Two Tailed Test
Alternative hypothesis
having two sides.
H0: µ = µ0 vs Ha µ ≠ µ0.
Reject H0 if
TS > TV or TS < –TV
1. State the hypothesis.
2. Identify the appropriate
test statistic and its
probability distribution.
3. Specify the significance
level.
4. State the decision rule.
5. Collect the data &
calculate the test statistic.
6. Make the statistical
decision.
7. Make the economic or
investment decision.
(Source: Wayne W. Daniel
and James C. Terrell, Business
Statistics, Basic Concepts and
Methodology, Houghton
Mifflin, Boston, 1997.)
Test Statistics
Statistical Significance vs
Economical Significance
Statistically significant results
may not necessarily be
economically significant.
A very large sample size may
result in highly statistically
significant results that may be
quite small in absolute terms.
Hypothesis testing involves
two statistics:
TS calculated from
sample data.
Critical values of TS.
Two Types of
Errors
Type I Error
Rejecting a
true null
hypothesis.
Type II Error
Failing to reject a
false null
hypothesis.
Decision Rule
Based on comparison of TS to
specified value(s).
It is specific & quantitative.
Copyright © FinQuiz.com. All rights reserved.
Significance
Level (α )
Probability of
making a type I
error.
Denoted by
Greek letter
alpha (α ).
Used to identify
critical values.
2017, Study Session # 3, Reading # 12
σ 2 = Population Variance
N.Dist = Normally Distributed
N.N.Dist = Non Normally Distributed
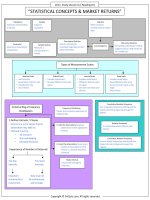
Relationship b/w Confidence Intervals &
Hypothesis Tests
Related because of critical value.
C.I
[(SS)- (CV)(SE)] ≤ parameter ≤ [(SS) + (CV)(SE)].
It gives the range within which parameter value
is believed to lie given a level of confidence.
Hypothesis Test
-C V ≤ TS ≤ + CV.
Range within which we fail to reject null
hypothesis of two tailed test at given level of
significance.
Testing
•
Population Mean
•
•
•
•
•
σ2 known
N. dist.
ݖ
n ≥30
σ2 unknown
Decision Rule
x −µ 0
z=
σ
•
n
௫̅ ିఓ
= ௦ బ
ൗ
√
σ2 unknown
n<30
N. dist.
t n−1 =
Unknown variances
assumed equal.
+
1
σ
−
2
n n 2
•
n
)
=
•
; df = n-1
t=
Populations based
on Independent
Unequal unknown
variances.
Ho:µ = µ0 vs Ha: µ ≠µ0
Reject H0 if TS > TV or TS < – TV
( x1 − x2 ) − ( µ1 − µ 2 )
1 1
sP
+
n1 n2
•
( n1 − 1) s1 + ( n2 − 1) s 2
n1 + n2 − 2
2
Ho:µ1 - µ2 ≤ 0 vs Ha: µ1 -µ2 > 0
2
Reject H0 if TS > TV
df = n1+n2 - 2
Distributed
Ho:µ > µ0 vs Ha: µ <µ0
Reject H0 if TS < –TV
where;
sP =
Normally
x − µ0
Ho:µ ≤ µ0 vs Ha: µ >µ0
Reject H0 if TS > TV
௫̅ ିఓ
∗
or ݐିଵ
= ௌ/ బ
√
*(more conservative)
Means of Two
Samples.
Power of a Test
1 – P(type II error).
Probability of correctly rejecting
a false null hypothesis.
Test Statistics
t(
Equality of the
p- value
The smallest level of significance
at which null hypothesis can be
rejected.
Reject H0 if p-value < α.
Conditions
•
df = Degree of Freedom
n ≥ 30 = Large Sample
n< 30 = Small Sample
n = Sample Size
( x1 − x 2 ) − ( µ1 − µ 2 )
•
Reject H0 if TS < -TV
s12 s 22
+
n1 n 2
2
s12 s22
+
n n
d . f = 12 2 2
s12
s22
n1 + n2
n1
n2
Copyright © FinQuiz.com. All rights reserved.
Ho:µ1 - µ2 > 0 vs Ha: µ1 -µ2 < 0
•
Ho:µ1 - µ2 = 0 vs Ha: µ1 - µ2 ≠ 0
Reject H0 if TS > TV or TS < – TV
2017, Study Session # 3, Reading # 12
Paired Comparisons
Test
TS t(n-1 )=
ௗതିఓబ
௦
ഥ
TS
ଶ
߯ሺିଵሻ
1
݀̅ = . ݀
݊
ୀଵ
Sୢഥ =
ݏௗ
=ඨ
Testing Variance of a
N.dist. Population
Sୢ
√n
∑ୀଵ(݀ − ݀̅ )ଶ
݊−1
=
ሺ݊ − 1ሻ ݏଶ
ߪଶ
Decision Rule
Reject H0 if TS > TS
Chi-Square
Distribution
Asymmetrical.
Bounded from below
by zero.
Chi-Square values
can never be –ve.
Testing Equality of
Two Variances from
N.dist. Population
TS
=ܨ
ௌభమ
;ܵଵଶ
ௌమమ
> ܵଶଶ
Parametric Test
Specific to population
parameter.
Relies on assumptions
regarding the distribution of
the population.
Non-Parametric Test
Decision Rule
Reject H0 if TS > TV
F- Distribution
Right skewed.
Bounded by zero.
Decision Rule
H0: µd ≤ µd0 vs Ha: µd > µd0
Reject H0 if TS > TV.
H0: µd ≥ µd0 vs Ha:µd < µd0
Reject H0 if TS <-TV
H0: µd = µd0 vs Ha: µd ≠ µd0
Reject H0 if TS > TV.
Copyright © FinQuiz.com. All rights reserved.
Do not consider a particular
population parameter.
Or
Have few assumptions
regarding population.