WebSphere Studio Application Developer Version 5 Programming Guide part 16 ppsx
Bạn đang xem bản rút gọn của tài liệu. Xem và tải ngay bản đầy đủ của tài liệu tại đây (205.42 KB, 10 trang )
124 WebSphere Studio Application Developer Version 5 Programming Guide
Refactoring preferences
In the Refactoring preferences page, located in
Window -> Preferences -> Java
-> Refactoring
, you can select the default level for problems to be displayed when
you are carrying out a refactoring without a preview (Figure 5-29).
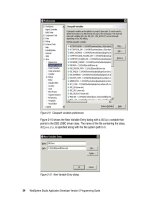
Figure 5-29 Refactoring preferences
The set of radio buttons is used to indicate what type of error reporting you want
to see in the refactoring dialog. These options are listed in order of severity. By
default Application Developer will display any error that would occur if the
refactoring is performed.
If you check the option
Save all modified resources automatically prior to
refactoring
, any outstanding changes will be saved without displaying a prompt.
Refactoring example
The following example of a refactoring operation assumes that you want to
rename a class in your Java program. To initiate the renaming, simply select the
class and select
Refactor -> Rename
in the context menu. The Refactoring
wizard is displayed, where you rename the class and select the appropriate
refactoring settings (Figure 5-30).
Chapter 5. Developing Java applications 125
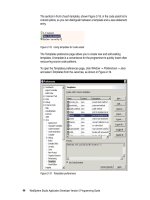
Figure 5-30 Refactoring wizard
Enter the new name for the class and click
Next
. If there are any files with
unsaved changes in the Workbench and you have not indicated in the
preferences that the save should be done automatically, you are prompted to
save these files before continuing the refactoring operation.
If problems more severe than the default level set in the refactoring preferences
are anticipated, then the problems page is displayed (Figure 5-31). If the
problems are severe, the
Next
and
Finish
buttons are disabled and the
refactoring must be aborted until the problems have been corrected. If the
buttons are enabled, you can select whether to accept the problems and
continue, or to cancel the refactoring operation.
Figure 5-31 Refactoring problems
Selecting
Next
at this point displays a window showing what actions will be
performed during the refactoring (Figure 5-32).
126 WebSphere Studio Application Developer Version 5 Programming Guide
Figure 5-32 Refactoring preview
After reviewing the changes that will be applied, you can again select whether to
Finish
or to
Cancel
the refactoring operation. Clicking
Finish
will perform the
renaming operation of the class. If there are any problems detected, they will be
displayed after the operation has been completed. The type of problem shown
depends on the settings in the Refactoring preferences dialog (Figure 5-29 on
page 124).
Application Developer provides one level of an undo operation for refactoring
commands. If you want to undo the renaming changes at this point, select
Refactor -> Undo
from the menu bar.
Code generation actions
Application Developer’s Java editor allows you to generate default Java code. It
can generate getters and setters, override methods, or add constructors from the
superclass.
Chapter 5. Developing Java applications 127
Generate getters and setters
When working with the Java editor you can generate accessors (getters and
setters) for the fields of a type inside a compilation unit. There are several ways
to generate getters and setters for a field:
Select
Source -> Generate Getter and Setter
from the context menu in the
Java editor.
Select
Source -> Generate Getter and Setter
from the context menu of the
field in the Outline view.
Select
Source -> Generate Getter and Setter
from the menu bar.
A dialog opens to let you select which methods you want to create. Select the
methods and click
OK
(Figure 5-33).
Figure 5-33 Generate Getter and Setter dialog
Override methods
The override methods feature helps you to override methods from the
superclass. Select
Source -> Override Methods
from the menu or
Override
Methods
in the context menu of a selected type or on a text selection in a type.
The Override Methods dialog (Figure 5-34) displays all methods that can be
overridden from superclasses or implemented from interfaces. Abstract methods
or not yet implemented methods are selected by default.
When clicking
OK
, method stubs for all selected methods are created.
128 WebSphere Studio Application Developer Version 5 Programming Guide
Figure 5-34 Override methods dialog
Add constructors from superclass
This feature allows you to automatically add constructors as defined in the
superclass for the currently selected type. Open the context menu in the Java
editor and select
Source -> Add Constructors from Superclass
.
Smart compilation
The Java Builder in the Workbench incrementally compiles the Java code as it is
changed, unless you disable the automatic build feature. For more information
consult the section “Automatic builds” on page 27.
Java search and working sets
In addition to the normal text search functionality, Application Developer provides
a special Java element search feature. Using the Java Search dialog, you can
search for types, methods, packages, constructors and fields within the
workspace. The search results can be limited to show only declarations,
references, implementors or read or write access if you are searching for a
specific field.
You can also specify the scope of the search. You can either search the
workspace, choose only the selected resources or create a working set, which
can be used for future searches as well.
Chapter 5. Developing Java applications 129
Working sets are used, because users often find it necessary to filter views such
as the navigator view in order to reduce clutter. Working sets can be used to filter
resources by only including specified resources. They are selected and defined
using the view's filter selection dialog.
Simply click the
Search
icon to open the search dialog. Figure 5-35
demonstrates how to search for the field dbtab within a working set.
Figure 5-35 Java search dialog
Type in the search string, specify that you would like to search for a field, and
select
Working Set
as the scope of this search.
Click
Choose
to display a new dialog, where you can select an existing working
set or create a new one (Figure 5-36).
Click
New
to create a new working set. Select a Resource working set or a
Java working set and click
Next
.
The last page of the wizard is displayed. You have to name your new working
set and specify the working set content.
Click
Finish
to create the working set.
130 WebSphere Studio Application Developer Version 5 Programming Guide
Figure 5-36 Creating a working set
By confirming this dialog with
OK
, the new set will be used in our Java search.
Figure 5-37 shows the Java search dialog with the new working set. Click
Search
to start the search operation.
Select the
projects or
folders of the
working set
Chapter 5. Developing Java applications 131
Figure 5-37 Java search dialog with Working Set
The search results are displayed in the Search view (Figure 5-38).
Double-clicking the result entry in the Search view opens the source file where
the field has been found and the first match is highlighted. The yellow arrows on
the left hand side indicate the lines where a match has been found.
Figure 5-38 Java search results
132 WebSphere Studio Application Developer Version 5 Programming Guide
Bookmarks
Bookmarks are a simple way to navigate to resources that you frequently use.
The Bookmarks view displays all bookmarks in the Workbench. To show the
Bookmarks view choose
Window -> Show View -> Other
and select
Bookmarks
from the Basic section.
To set a bookmark in your code, right-click in the gray sidebar left of your code in
the Java editor and select
Add Bookmark
(Figure 5-39).
Figure 5-39 Adding a bookmark
A dialog is displayed where you have to enter a name for the new bookmark
(Figure 5-40).
Figure 5-40 Naming a bookmark
Chapter 5. Developing Java applications 133
The newly created bookmark is indicated by a symbol in the marker bar and also
appears in the Bookmarks view. Double-clicking the bookmark entry in the
Bookmarks view opens the file and navigates to the line where the bookmark has
been created.
You can remove a bookmark by using the bookmark’s context menu in the
Bookmarks view and select
Delete
.
Javadoc
Javadoc is a tool in the Java JDK to generate documentation about Java
packages, classes, and methods. The Javadoc documentation is based on
comments entered for each class and method, and the packaging of classes into
packages.
Preferences
The location of the javadoc.exe must be specified in the Javadoc preferences.
Refer to “Javadoc documentation” on page 40 for instructions.
Generating Javadoc
Application Developer provides a wizard to generate Javadoc for selected
packages or projects.
In this section we generate Javadoc for the ItsoProGuideJava project:
Select the ItsoProGuideJava project and
Export
(context).
Select
Javadoc
and click
Next
.
Select the projects (or expand and select packages), member visibility, and
the output location. The default location is in the workspace (Figure 5-41).
Click
Next
.
Tip: You can bookmark individual files in the Workbench to open them quickly
from the Bookmark’s view later. In the Navigator view, right-click the file that
you want to add to you list of bookmarks and select
Add Bookmark
from the
file’s pop-up menu.
Note: Bookmarks are not specific to Java code. They can be used in any file
to provide a quick way of navigating to a specific location.